How to Live an Anti-Inflammatory Lifestyle
Inflammation. It’s a word that’s often associated with pain and discomfort. But did you know it also plays a crucial role in your health and fitness journey?
Chronic inflammation can be a silent saboteur, undermining your hard-earned fitness gains. It’s linked to a host of diseases, from heart disease to diabetes, and can hamper athletic performance and recovery.

But there’s good news. By adopting an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, you can combat chronic inflammation and enhance your overall wellbeing. This involves making mindful choices about what you eat, how you move, and how you manage stress.
In this article, we’ll delve into the world of anti-inflammatory living. We’ll explore the role of diet, the importance of hydration, and the impact of lifestyle factors like sleep and stress.
Whether you’re a seasoned fitness enthusiast or just starting your wellness journey, this guide will provide you with the tools to live a vibrant, anti-inflammatory lifestyle. Let’s embark on this journey together.
Understanding Chronic Inflammation and Its Effects on Health
Inflammation is a natural response of your body’s immune system. It’s a protective mechanism designed to fight off infections and heal injuries. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can wreak havoc on your health.
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged, low-grade inflammation that can last for months or even years. Unlike acute inflammation, which is a short-term response to injury or infection, chronic inflammation often has no visible symptoms. This makes it particularly insidious and damaging.
Chronic inflammation is linked to a host of diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. It can also impact your fitness journey by hampering athletic performance and slowing down recovery. This is because chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and disrupt normal cellular processes.
But the good news is, you have the power to combat chronic inflammation. By adopting an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, you can reduce inflammation and its harmful effects on your health and fitness. In the following sections, we’ll explore how you can do this through diet, hydration, and lifestyle modifications.
The Connection Between Diet and Inflammation
Your diet plays a crucial role in managing inflammation. Certain foods can trigger inflammation, while others can help reduce it. Understanding this connection is key to adopting an anti-inflammatory lifestyle.
Inflammatory foods are typically those that are processed, high in sugar, and low in nutrients. These foods can trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation. On the other hand, anti-inflammatory foods are usually whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in antioxidants and other nutrients.
Antioxidants are compounds that help neutralize harmful free radicals in your body. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage and inflammation if left unchecked. By consuming a diet rich in antioxidants, you can help combat inflammation at the cellular level.
Fiber is another important dietary component for managing inflammation. It helps regulate your gut health, which plays a crucial role in your body’s immune response and inflammation levels. A diet rich in fiber can help maintain a healthy gut and reduce inflammation.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the specific foods you should incorporate into your diet and those you should avoid to manage inflammation.
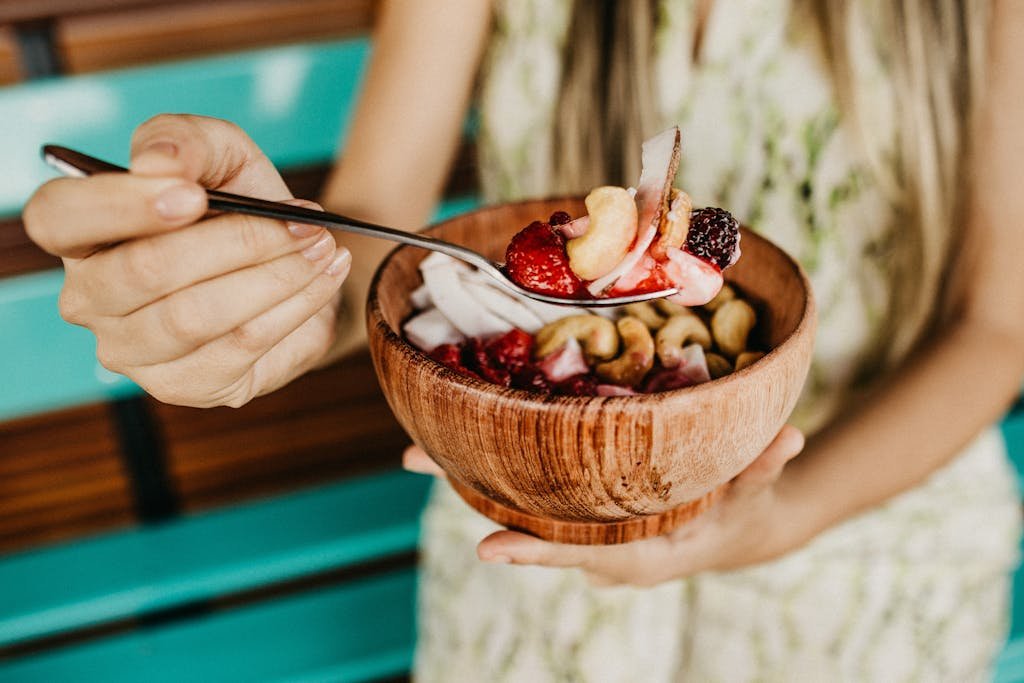

Anti-Inflammatory Foods to Incorporate into Your Diet
When it comes to fighting inflammation, not all foods are created equal. Some foods are particularly potent in their anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help you manage inflammation and support your overall health.
Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale, are rich in antioxidants and fiber. They help neutralize free radicals and support gut health, making them excellent for fighting inflammation.
Berries, such as blueberries and strawberries, are another great choice. They’re packed with antioxidants and other nutrients that can help reduce inflammation.
Fatty fish, like salmon and mackerel, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s are known for their powerful anti-inflammatory effects. They can help reduce inflammation and support heart health.
Spices like turmeric and ginger also have potent anti-inflammatory properties. They contain compounds that can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
Probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt and fermented foods, can also help manage inflammation. They support gut health, which plays a crucial role in your body’s immune response and inflammation levels.
Hydrating foods, like cucumbers and watermelon, can also support an anti-inflammatory lifestyle. Hydration is key to flushing out toxins and reducing inflammation.
Here’s a list of some anti-inflammatory foods to incorporate into your diet:
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale)
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries)
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
- Spices (turmeric, ginger)
- Probiotic-rich foods (yogurt, fermented foods)
- Hydrating foods (cucumbers, watermelon)
Remember, variety is key. Try to incorporate a diverse range of anti-inflammatory foods into your diet to ensure you’re getting a wide array of nutrients.
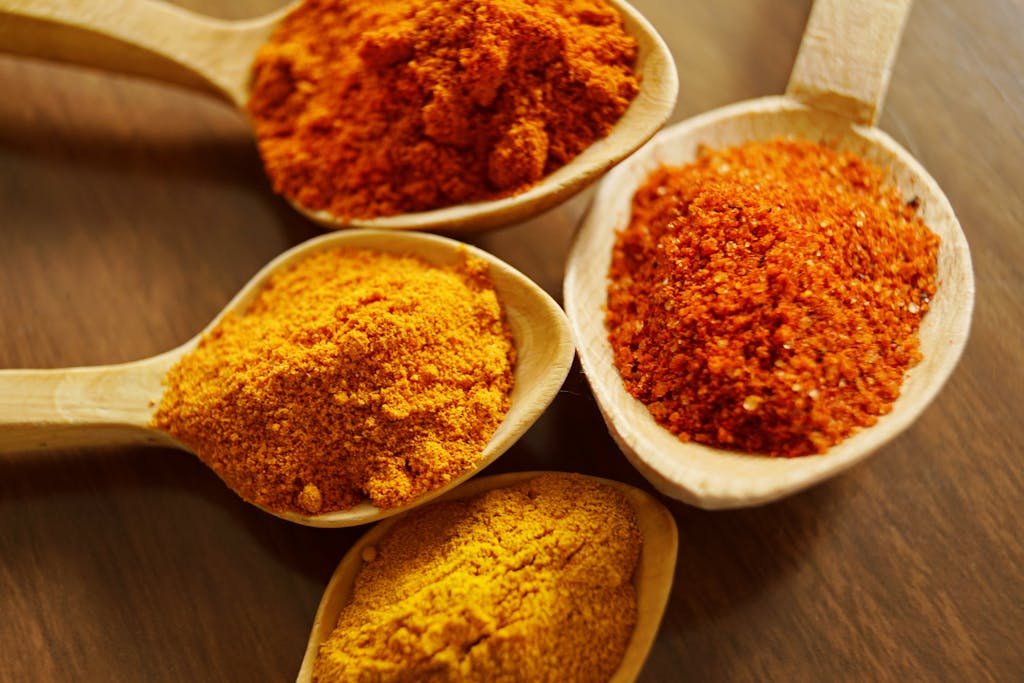

Foods to Avoid That May Trigger Inflammation
Just as there are foods that can help reduce inflammation, there are also foods that can trigger it. These are typically processed foods that are high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives.
Processed foods, such as chips and cookies, are often high in trans fats and refined sugars. These can trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation.
Refined carbohydrates, like white bread and pasta, can also contribute to inflammation. They’re low in fiber and can lead to spikes in blood sugar, which can trigger an inflammatory response.
Sugary drinks, like soda and energy drinks, are another culprit. They’re high in sugar and can contribute to inflammation and other health issues.
Alcohol and tobacco can also trigger inflammation. They can disrupt normal cellular processes and lead to tissue damage and inflammation.
Here’s a list of some foods and substances to avoid or limit to manage inflammation:
- Processed foods (chips, cookies)
- Refined carbohydrates (white bread, pasta)
- Sugary drinks (soda, energy drinks)
- Alcohol
- Tobacco
Remember, moderation is key. It’s okay to indulge in these foods occasionally, but try to limit your intake to maintain a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet.
The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Antioxidants
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of fat that your body can’t produce on its own. They’re essential for your health and have powerful anti-inflammatory effects. Foods rich in omega-3s, like fatty fish and flaxseeds, can help reduce inflammation and support heart health.
Antioxidants, on the other hand, are compounds that help neutralize harmful free radicals in your body. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause cellular damage and inflammation if left unchecked. Foods rich in antioxidants, like berries and leafy greens, can help combat inflammation at the cellular level.
Incorporating both omega-3s and antioxidants into your diet is key to managing inflammation. They each play a unique role in supporting your health and fighting inflammation.
Remember, a balanced diet that includes a variety of anti-inflammatory foods is the best way to ensure you’re getting enough omega-3s and antioxidants.

Gut Health and Its Impact on Inflammation
Your gut health plays a crucial role in your overall health and wellbeing. It’s home to trillions of bacteria, both good and bad, that influence many aspects of health, including inflammation. A healthy gut is characterized by a balance of these bacteria, known as your gut microbiota.
When this balance is disrupted, it can lead to a condition known as dysbiosis. Dysbiosis has been linked to increased inflammation and several health conditions, including obesity, heart disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Probiotics, or beneficial bacteria, can help restore this balance and reduce inflammation. They can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, and kimchi, or taken as supplements.
Maintaining a healthy gut is a key component of an anti-inflammatory lifestyle. It’s important to nourish your gut with a balanced diet, rich in fiber and probiotics, to support a healthy microbiota and reduce inflammation.
Hydration: A Key Component of an Anti-Inflammatory Lifestyle
Hydration is a fundamental aspect of an anti-inflammatory lifestyle. Water plays a vital role in flushing out toxins from the body, which can contribute to inflammation.
Drinking adequate amounts of water can also support digestion and nutrient absorption. This is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut, which, as we’ve discussed, plays a key role in managing inflammation.
Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day. Remember, your hydration needs may increase with physical activity or in hot weather. Always listen to your body and drink when you’re thirsty.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Inflammation: Stress and Sleep
Inflammation is not solely influenced by diet. Lifestyle factors, such as stress and sleep, also play a significant role. Chronic stress can trigger an inflammatory response in the body, negatively impacting your health.
Similarly, lack of quality sleep can contribute to inflammation. Sleep is a restorative process for the body, and disruptions can lead to increased inflammatory markers.

Strategies for Stress Management
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining an anti-inflammatory lifestyle. Regular physical activity can help reduce stress levels and promote a sense of well-being.
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and yoga, can also be beneficial. These practices can help you stay present and reduce feelings of stress.
Lastly, maintaining a strong social network can provide emotional support and help manage stress.
The Importance of Quality Sleep
Quality sleep is as important as diet in an anti-inflammatory lifestyle. Aim for seven to nine hours of sleep per night to allow your body to rest and recover.
Poor sleep can disrupt the balance of hormones in your body, leading to inflammation. Therefore, establishing a regular sleep schedule and creating a restful environment can support better sleep.
Remember, quality sleep is not just about duration. It’s also about the depth and continuity of your sleep.
Exercise: A Potent Anti-Inflammatory Tool
Regular physical activity is a powerful tool in combating inflammation. Exercise stimulates the production of anti-inflammatory substances in the body, promoting overall health.
However, the type and intensity of exercise matter. Moderate-intensity activities, such as brisk walking or cycling, can be particularly beneficial. These activities can be easily incorporated into your daily routine.
High-intensity workouts also have their place, but balance is key. Overtraining can lead to increased inflammation, so it’s important to allow your body time to recover.
Remember, consistency is more important than intensity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by health experts. This can be broken down into manageable sessions throughout the week.
Personalizing Your Anti-Inflammatory Lifestyle
Adopting an anti-inflammatory lifestyle is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Each individual’s body responds differently to foods and lifestyle changes. Therefore, personalization is key.
Consider your unique fitness goals and dietary needs. For instance, if you’re a marathon runner, your diet may need to be higher in carbohydrates than someone who is sedentary.
Also, consider your personal food preferences and cultural background. An anti-inflammatory diet should be enjoyable and sustainable, not restrictive or boring.
Remember, the goal is to make long-term changes that support your overall health and wellbeing. It’s not about perfection, but progress.

Tailoring Diet to Fitness Goals
Your fitness goals play a crucial role in shaping your anti-inflammatory diet. For instance, if your goal is to build muscle, you’ll need adequate protein.
However, it’s not just about quantity, but quality. Choose lean proteins and incorporate plenty of anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, nuts, and seeds.
Remember, balance is key. Even if you’re trying to gain muscle or lose weight, your body still needs a variety of nutrients to function optimally and combat inflammation.
Conclusion: Embracing a Holistic Approach to Inflammation
Living an anti-inflammatory lifestyle goes beyond just diet and exercise. It’s about embracing a holistic approach to health that includes stress management, quality sleep, and a positive mindset.
Remember, consistency is key. It’s the small, daily habits that make the biggest difference over time. So, start small and gradually incorporate more anti-inflammatory habits into your lifestyle.
In the end, it’s not just about reducing inflammation. It’s about enhancing your overall wellbeing, boosting your performance, and living a vibrant, healthy life. Embrace the journey and celebrate each step towards your healthiest self!






One Comment
Comments are closed.